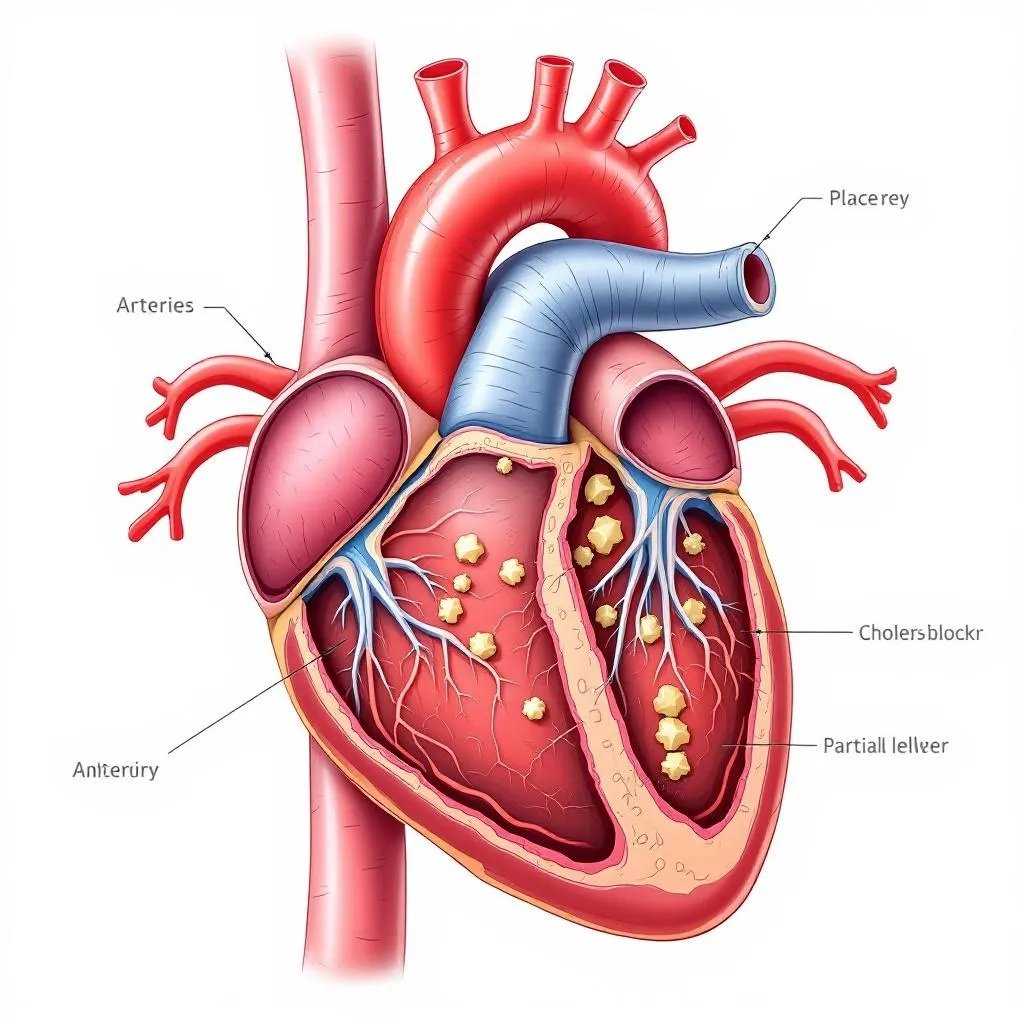
Atherosclerotic Heart Disease, also known as Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), is a leading cause of heart-related complications worldwide. It occurs due to the buildup of plaque—composed of fat, cholesterol, and other substances—in the coronary arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow to the heart. This can result in chest pain, shortness of breath, heart attack, or sudden cardiac death.
Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, implementing prevention strategies, and knowing the treatment options are essential for maintaining optimal heart health. For more guidance, explore our Healthy Diet and Prevention & Lifestyle sections.
Causes and Risk Factors of Atherosclerotic Heart Disease
Plaque Buildup in Arteries
Progressive plaque accumulation, or atherosclerosis, is the main cause of CAD. Over time, arteries narrow or become blocked, increasing the risk of heart attack.
High Cholesterol & LDL
High LDL (“bad”) cholesterol contributes to plaque formation, while low HDL (“good”) cholesterol reduces the body’s ability to remove excess cholesterol. Learn more at Mayo Clinic.
High Blood Pressure
Hypertension damages arterial walls, making them more prone to plaque accumulation. Controlling blood pressure is critical in preventing CAD.
Smoking & Diabetes
Smoking accelerates plaque formation, while diabetes damages blood vessels due to high blood sugar levels. Visit our Prevention & Lifestyle section for detailed strategies.
Additional Risk Factors
- Obesity and overweight
- Family history of heart disease
- Chronic stress and poor sleep
- Physical inactivity
Symptoms of Atherosclerotic Heart Disease
Chest Pain (Angina)
Angina is caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle. Patients experience pressure, squeezing, or discomfort in the chest.
Shortness of Breath
Decreased blood flow can lead to difficulty breathing during activity or even at rest.
Fatigue and Weakness
Poor oxygen delivery to tissues may result in persistent fatigue and general weakness.
Heart Attack Warning Signs
Sudden chest pain, discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach, and nausea may indicate a heart attack. Read more at American Heart Association.
Potential Complications
- Heart Attack: Complete blockage of a coronary artery leading to permanent heart damage.
- Heart Failure: Long-term CAD can weaken the heart muscle, reducing its pumping efficiency.
- Arrhythmia: Damage to heart tissue can cause abnormal heart rhythms.
Explore our Treatments & Remedies section to manage these complications.
Diagnosis of Atherosclerotic Heart Disease
- Blood tests to measure cholesterol, triglycerides, and cardiac markers
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to detect irregular heart rhythms
- Stress tests to assess heart performance under exertion
- Coronary angiography to visualize blockages Source: WebMD
Prevention & Lifestyle Modifications
Heart-Healthy Diet

Eating a balanced diet helps reduce plaque buildup. Key foods include:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins
- Omega-3 rich foods such as salmon and flaxseed
Learn more in our Healthy Diet section.
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days improves circulation and heart function.
Quitting Smoking
Eliminating tobacco use significantly reduces the risk of artery damage and heart disease.
Managing Cholesterol & Blood Pressure
Consistent monitoring and treatment of cholesterol levels and blood pressure are vital preventive measures.
Treatment Options for Atherosclerotic Heart Disease
Medications
- Statins to lower cholesterol
- Beta-blockers to reduce heart workload
- Aspirin to prevent clot formation
Surgical Interventions
- Angioplasty and stent placement to open blocked arteries
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) in severe cases
Natural Remedies & Supplements
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Antioxidants such as Vitamin C and E
- Lifestyle modifications including stress management and adequate sleep
Further reading: Healthline – Heart Disease Treatments
Atherosclerotic Heart Disease is serious but preventable and manageable. Recognizing early symptoms, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, and seeking appropriate medical treatment can significantly reduce risks.
Explore our Prevention & Lifestyle and Healthy Diet sections for more guidance on protecting your heart. Taking proactive steps today ensures a healthier heart tomorrow.